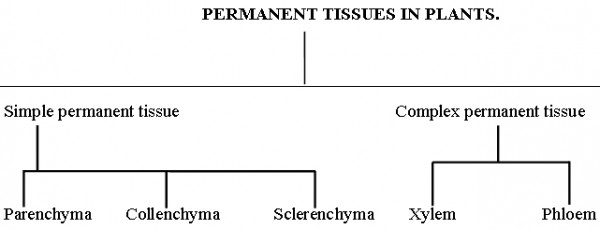
There are two types of permanent tissues in plants.
1. Simple permanent tissues
(made up of only one type of cells).
These include:
|
Name of tissue
|
Structure
|
Occurrence
|
Function
|
|
Parenchyma
|
- Cells living.
- Spherical in shape.
- Nucleus present.
- Thin cellulose wall.
- Intermolecular spaces
present.
|
Cortex of root,
Mesophyll of leaf,
Ground tissue of stem.
|
Storage of food (eg. Potato).
Temporary support.
|
|
Collenchyma
|
- Cells living.
- Nucleus present.
- Elongated in shape.
- Unevenly thickened
with cellulose at
corners.
- Little intercellular
space.
|
Below epidermis of stem,
Leaf stalks.
|
Flexibility and support to leaves and stem.
Mechanical support.
|
|
Sclerenchyma
|
- Cells are dead.
- Nucleus absent.
- Elongated and narrow.
- Lignin deposition.
- Reduced lumen.
- Vacuole absent.
|
Hard covering of seeds,
In stems around vascular bundles.
|
Mechanical strength and support to the plant.
|
2. Complex permanent tissues
(made up of different types of cells)
These include:
a. Xylem:
-
It forms the main mechanical tissue in the form of wood.
-
It consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma.
-
It conducts water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
b. Phloem:
-
It consists of sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
-
It conducts organic solutes from storage parts to other regions.
-
It conducts food from the leaves to other non-green parts of the plant.