Sex determined in human beings
-
Determination of sex in human beings is done by their sex chromosomes.
-
Females have XX chromosomes in their somatic cells whereas, males have XY chromosomes.
-
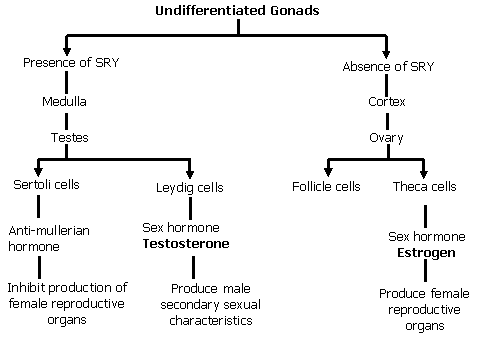
Development of functional testes is present in males.
-
These testes are induced by the activity of TDF (Testes Determining Factor).
-
TDF is encoded by SRY (Sex Determining Region) that is located on the short arm of Y chromosome.
-
This SRY is the only gene present at Y chromosome, which is necessary to initiate development of testes and expressed only in the cells that develop gonad.
-
Expression of these genes in somatic cells differentiates the cells itself into “sertoli cells”.
-
Sertoli cells are the supporting cells in testes that produce “anti-mullerian hormone”.
-
This hormone suppresses the development of female reproductive organs.
-
Sertoli cells also induce the development of “Leydig cells” from somatic cells that secrete the male sex hormone “Testosterone”.
-
Now, in the absence of SRY gene, the somatic cells that develop gonad develop into “Ovary” and the supporting cells become “follicle cells”.
-
The other somatic cells become “Theca cells” and secrete the female sex hormone “estrogen”.
-
The male sex hormone is responsible to induce male secondary sexual characteristics.
-
The below chart is the summary of the sequences involved in the human sex determination: