PROTOPLAST FUSION
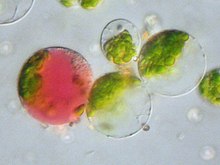 The term ‘protoplast’ represents the naked living contents of a cell without the cell wall. The fusion of two protoplasts from two different species is called Protoplast fusion. It is also called as Somatic Hybridization.
The term ‘protoplast’ represents the naked living contents of a cell without the cell wall. The fusion of two protoplasts from two different species is called Protoplast fusion. It is also called as Somatic Hybridization.
As the isolated protoplasts are devoid of cell walls, their in vitro fusion becomes relatively simpler and easier since there are no barriers of incompatibility.
Protoplast fusion involves mixing of protoplasts from two different genomes and their fusion is carried out by spontaneous, mechanical or induced fusion techniques.
The chemicals which promote fusion of protoplasts are called fusogenic agents. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is the most widely used one. It causes rapid agglutination and formation of clumps of protoplasts. This leads to the formation of tight adhesions of membranes and ultimately their fusion. Fusion mainly involves formation of cytoplasmic bridges between protoplasts.
REFERENCE
-
Image: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f8/Protoplast_fusion.jpg/220px-Protoplast_fusion.jpg