Mitochondria (singular, mitochondrion) are called the power-house of the cell, for it is within them that the energy is released from organic molecules by the process of cellular respiration.
Mitochondria convert organic molecules into energy for the cell.
It is responsible for the production of energy in the form of ATP which is gained by digestion, absorption and respiration in the cell.
Mitochondria are surrounded by a double-membrane system - an inner membrane and an outer membrane. The folds of the inner membrane, which is called cristae, are the site of energy conversion. Mitochondria are typically shaped like cucumber, rods or ball.
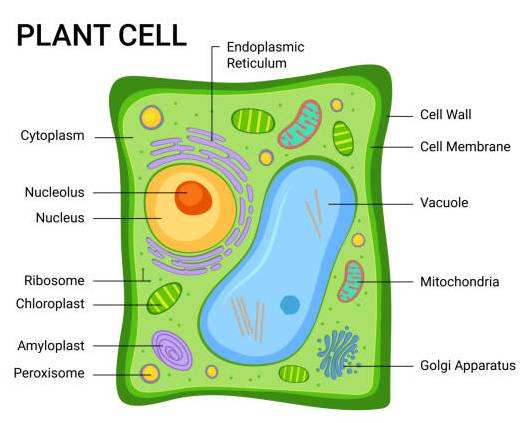
Plants need energy to keep the individual cells and the plant functioning. In plants carbon skeletons & fatty acid chains are also rearranged within mitochondria as it allows for the building of organic molecules.
Mitochondria, numerous and tiny in numbers, undergo constant motion in living cells and accumulate in groups where energy is needed. They all originate from the division of existing mitochondria.